2025-02-07
Optimizing GMP and GC
1. Concurrency
- Tune
GOMAXPROCSbased on the number of CPU cores and workload characteristics. - Use Goroutines efficiently, avoiding excessive creation or leaks.
2. GC 调参
- GC 调参的意义是什么?
- 调整GC频率相当于给了一个 "内存 - 计算" 间的权重滑动条,附录-GOGC 模拟器代码可以模拟不同 GOGC 值下的 GC 效果。
- 如何调整 GC 参数?
- 通过调整
GOGC环境变量,可以控制 GC 的频率,100 表示新分配的内存相比当前内存翻了 100% 倍后触发 GC。 - 通过
debug.SetGCPercent函数,当堆内存使用量大于指定值时触发 GC。
- 通过调整
根据Go GC 官网文档中的描述,GC 会在堆大小达到 前完成:
- :当前存活的堆大小
- :栈大小 + 全局变量大小
- :环境变量,用于调整。
- :目标堆大小
下面是一个测试 GOGC 工作特性的例子:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
_ "net/http/pprof"
"os"
"runtime"
"runtime/debug"
"runtime/trace"
"time"
)
func main() {
f, err := os.Create("gc_trace.out")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("could not create memory profile: ", err)
}
defer f.Close()
if err = trace.Start(f); err != nil {
log.Fatal("could not start trace: ", err)
}
defer trace.Stop()
runtime.GC() // get up-to-date statistics
// Set GOGC to 100
debug.SetGCPercent(100)
fmt.Println("GOGC set to 100")
// After 3 seconds, set GOGC to 500
time.AfterFunc(time.Second*3, func() {
debug.SetGCPercent(500)
fmt.Println("GOGC set to 500")
})
// After 6 seconds, close automatic GC
time.AfterFunc(time.Second*6, func() {
debug.SetGCPercent(-1)
fmt.Println("GOGC set to -1")
})
// Start a goroutine to simulate workload
go func() {
for {
_ = make([]byte, 1<<20) // Allocate 1MB
time.Sleep(100 * time.Millisecond)
}
}()
// Keep the main function running
time.Sleep(time.Second * 10)
}
运行 go tool trace gc_trace.out 查看 heap 分配情况。
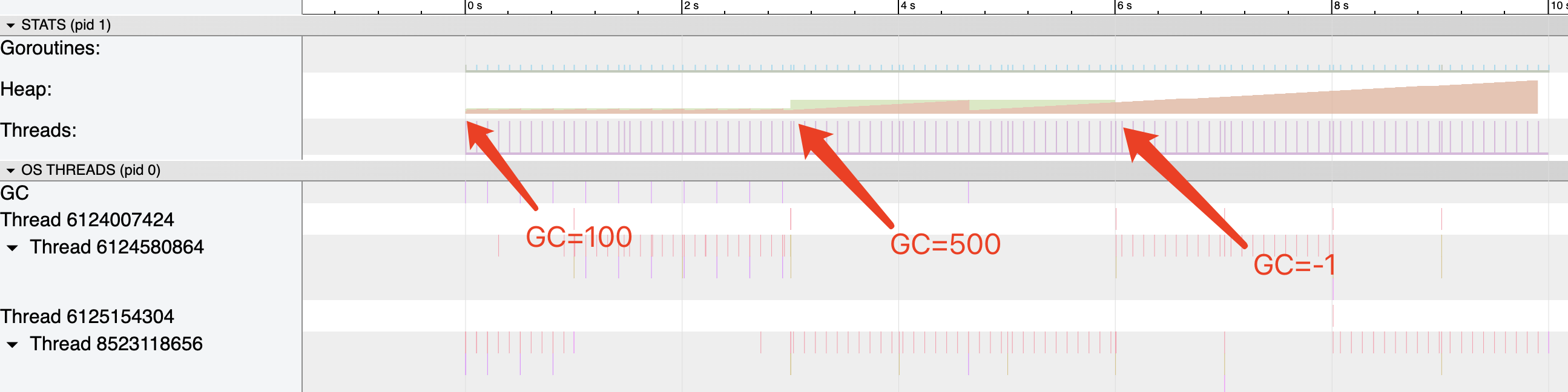
需要注意的是,GC释放的内存只是标记为可回收,实际并不会立即释放。
通过 debug.SetMemoryLimit、尽量使用 stack 内存、sync.Pool、预分配 slice 等方式,都可以减少 GC 的频率,提高程序性能。
附录
GOGC 模拟器代码
仅供演示,具体效果需要根据实际压测结果调整。
import pandas as pd
class GCSimulation:
gc_roots = 0 # MB, 栈 + 全局变量大小
live_heap_size = 10 # MB, 上次 GC 后的堆大小, 可通过 runtime.ReadMemStats 获取
marginal_heap_increase = 10 # MB, 每次 cpu-second 堆增长大小
gc_scan_speed = 100 # per cpu-second
gc_fix_cost = 0 # per cpu-second
GOGC = 100
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
for key, value in kwargs.items():
setattr(self, key, value)
@property
def target_heap_size(self):
return int(self.live_heap_size + (self.live_heap_size + self.gc_roots) * self.GOGC / 100)
@property
def gc_cpu_time(self):
gc_trigger_time = (self.target_heap_size - self.live_heap_size) / self.marginal_heap_increase
cpu_cost_per_gc = (self.gc_fix_cost + self.live_heap_size / self.gc_scan_speed)
return cpu_cost_per_gc / gc_trigger_time
def __str__(self):
return 'GCSimulation(heap_size={:<5d}cpu_cost={:<10.5f})'.format(self.target_heap_size, self.gc_cpu_time)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# create a data frame that has 'GOGC', 'heap_cost', 'cpu_cost' columns
df = pd.DataFrame(columns=['GOGC', 'heap_cost', 'cpu_cost', 'heap_marginal_cost', 'cpu_marginal_cost'])
data = []
for i in range(100):
if i == 0:
last_gc_simulation = GCSimulation(GOGC=100)
else:
last_gc_simulation = GCSimulation(GOGC=pow(2, i - 1) * 100)
gc_simulation = GCSimulation(GOGC=pow(2, i) * 100)
data.append(
{
'GOGC': gc_simulation.GOGC,
'heap_cost': gc_simulation.target_heap_size,
'cpu_cost': gc_simulation.gc_cpu_time,
'heap_marginal_cost': (gc_simulation.target_heap_size - last_gc_simulation.target_heap_size) / (last_gc_simulation.target_heap_size - last_gc_simulation.live_heap_size),
'cpu_marginal_cost': (gc_simulation.gc_cpu_time - last_gc_simulation.gc_cpu_time) / last_gc_simulation.gc_cpu_time,
}
)
df = pd.concat([df, pd.DataFrame(data)], ignore_index=True)
df.to_excel('gc_simulation_result.xlsx', index=False)